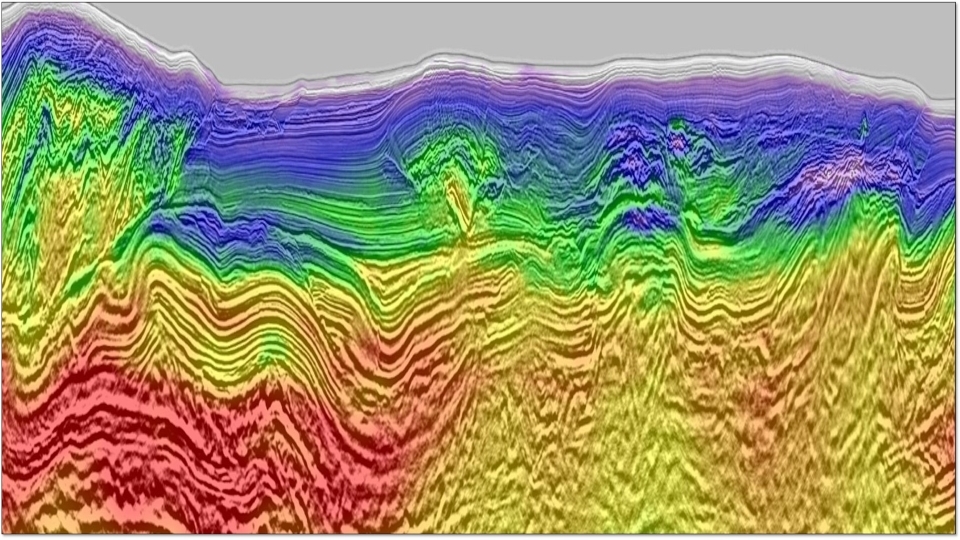
Gulf of Mexico (GOM) subsalt imaging often suffers from poor illumination due to salt-related wavefield distortion, even with full-azimuth (FAZ) acquisition. In order to image the weakly illuminated subsalt plays, isolating the signal from the noise is a crucial component of many depth imaging practices. Reverse Time Migration (RTM) subsurface 3D dip-azimuth gathers, which separate seismic data into different dip/azimuth components, have been utilized to address illumination problems in structure-oriented imaging techniques. We proposed a weighting scheme on RTM 3D dip gathers for imaging enhancement based on a priori structure information targeting the noise which has conflicting dips with the structure. We further discussed and evaluated the sensitivity of the method to the uncertainty of the priori structure dipping information. We applied the method on subsalt structures on a synthetic data set and a real data set with staggered acquisition full azimuth data. The tests demonstrated the necessity of signal-to-noise ratio enhancement in the imaging of FAZ, long-offset data and the effectiveness of RTM 3D dip gathers in unmasking poorly illuminated zones.
Download Resource 
Publications
The Leading EdgeAuthors
Yi Huang, Yang Li, Chang-chun Lee, Sabaresan Mothi, Yan Huang